What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) is a free and open technical specification that is used to authenticate an email by aligning SPF and DKIM mechanisms. By having DMARC in place, domain owners large and small can fight business email compromise, phishing, and spoofing.
With DMARC you can tell the world how to handle the unauthorized use of your email domains by instituting a policy in your DMARC record. The three DMARC policies are:
p=none
Monitors your email traffic. No further action is taken.
p=quarantine
Sends unauthorized emails to the spam folder.
p=reject
The final policy and the goal of implementing DMARC. This policy ensures that unauthorized email doesn’t get delivered at all.
How does DMARC work?
DMARC is based upon the results of SPF and/or DKIM, so at least one of those must be in place for the email domain. To deploy DMARC, you need to publish a DMARC record in the DNS.
A DMARC record is a text entry within the DNS record that tells the world your email domain’s policy after checking SPF and DKIM status. DMARC authenticates if either SPF, DKIM, or both passes. This is referred to as DMARC alignment or identifier alignment. Based on identifier alignment, it is possible that SPF and DKIM pass, but DMARC fails.
A DMARC record also tells email servers to send XML reports back to the reporting email address listed in the DMARC record. These reports provide insight on how your email is moving through the ecosystem and allow you to identify everything that is using your email domain.
Why Use DMARC for Email?
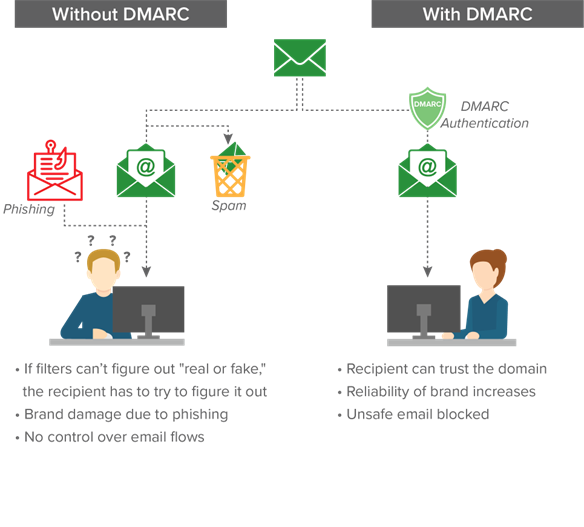
Email is involved in more than 90% of all network attacks and without DMARC, it can be hard to tell if an email is real or fake. DMARC allows domain owners to protect their domain(s) from unauthorized use by fighting phishing, spoofing, CEO fraud, and Business Email Compromise.
By always sending DMARC compliant email, the operator of an Internet domain can tell the world “Everything I send is easy to identify using DMARC—feel free to drop fake email that pretends to be me.”
DMARC’s utility as an anti-spoofing technology stem from a significant innovation; instead of attempting to filter out malicious email, why not provide operators with a way to easily identify legitimate email? DMARC’s promise is to replace the fundamentally flawed “filter out bad” email security model with a “filter in good” model.
If you’re curious about the health of your domain or anyone’s, use free Domain Checker websites for a quick check. It inspects DMARC, SPF and DKIM and tells you which actions you need to take to reach compliance.
Benefits of DMARC
Security
Disallow unauthorized use of your email domain to protect people from spam, fraud, and phishing.
Visibility
Gain visibility into who and what across the Internet is sending email using your email domain.
Delivery
Use the same modern plumbing that mega companies use to deliver email.
Identity
Make your email easy to identify across the huge and growing footprint of DMARC-capable receivers.
What is a DMARC TXT record?
Record for DMARC is a DNS text (TXT) record that helps prevent spoofing and phishing. You publish DMARC TXT records in DNS. DMARC TXT records validating the origin of email messages by verifying the IP address of an email’s author against the alleged owner of the sending domain. The DMARC TXT record identifies authorized outbound email servers. Destination email systems can then verify that messages they receive originate from authorized outbound email servers.
Microsoft’s DMARC TXT record looks something like this:
_dmarc.365cloudit.com. 3600 IN TXT “v=DMARC1; p=none; pct=100; rua=mailto:d@rua.365cloudit.com; ruf=mailto:d@ruf.365cloudit.com; fo=1”